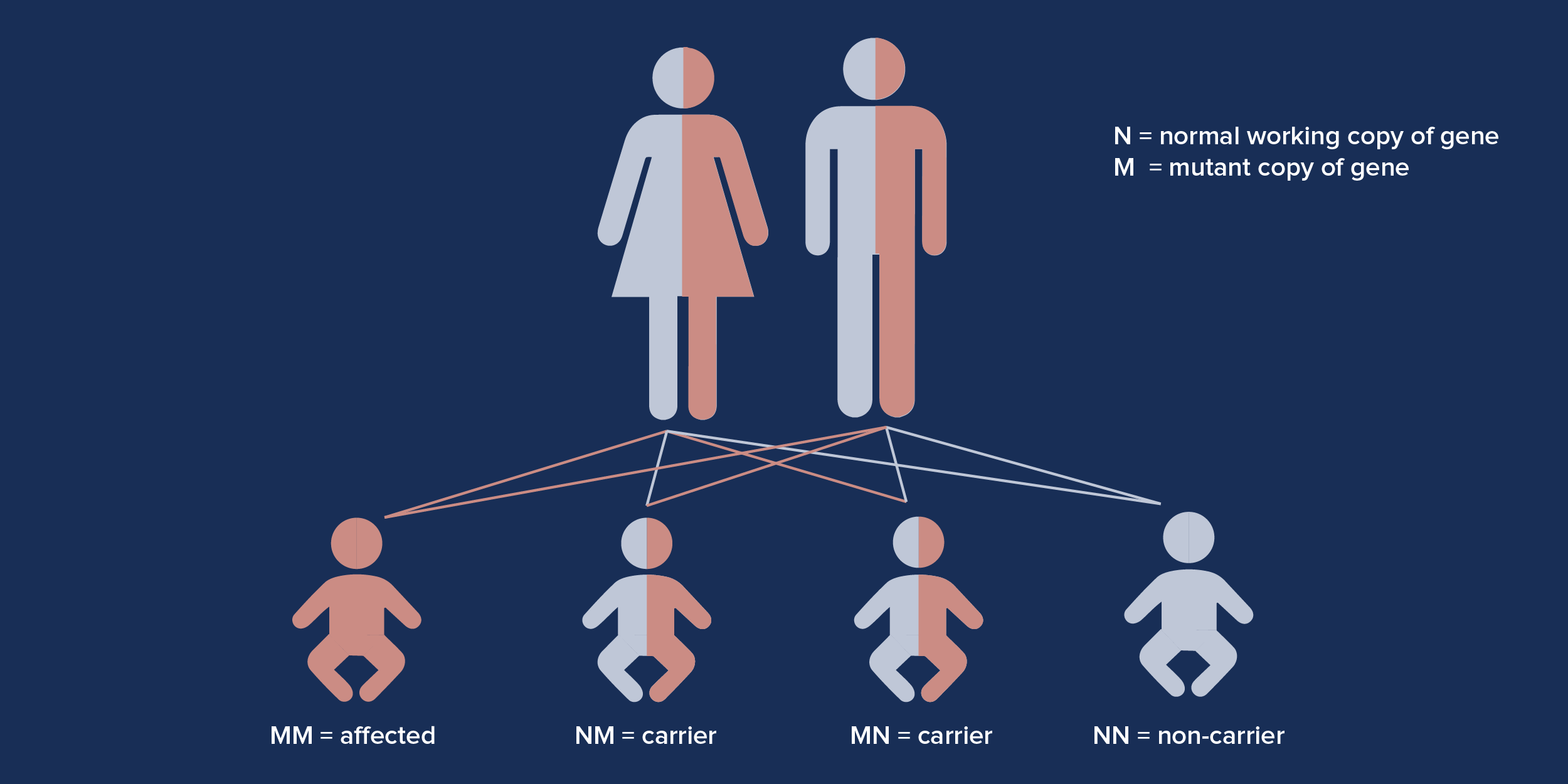
MVID is a congenital disease, meaning the baby is born with a genetic defect inherited from the parents. The defect is located in the gene MYO5B, which creates a protein called myosin VB. MVID is a congenital disease, meaning the baby is born with a genetic defect inherited from the parents. Genes come in pairs and each gene within the MYO5B pair must be defective for a person to show symptoms of MVID.
If only one of the genes in the pair is defective, the person is a “silent carrier” of MVID, and is not affected by the disease. For a baby to be born with MVID symptoms, he or she must get the defective gene from each parent. If both parents are “silent carriers,” there’s only a one in four chance the disease will affect the baby, as shown below: